- time:2021-10-12
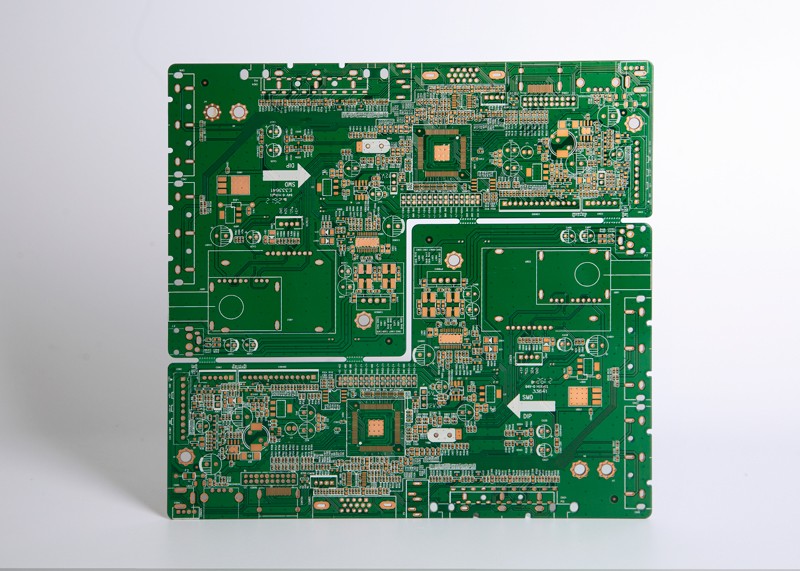
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a plastic laminated sandwich construction of copper and supporting layers. It consists of numerous copper pads or platers that are bonded to the substrate with soldering. Most printed circuit boards have two complementary
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a plastic laminated sandwich construction of copper and supporting layers. It consists of numerous copper pads or platers that are bonded to the substrate with soldering. Most printed circuit boards have two complementary purposes. First, the board functions as an assembly device to which various electronic components are affixed by soldering or fastening.
Secondly, the board helps in heat dissipation by providing a non-allergic barrier against the heated insides. Several printed circuit boards are made with aluminum-backed pcb's; however, high-quality aluminum-backed pcbs are available only from reliable manufacturers. Heat shrinkable aluminum-backed pcb's are a good option for those persons working with tight deadlines and budget constraints.
The construction of printed circuit boards is made on solid substrate like plastic, glass or metal. The two primary substrate choices are solid or semi-conductor materials like polyester, nylon, and polyester fiberglass. Solid substrate has better heat conduction and better conductivity. However, due to increased cost, solid substrate is generally used in low volume production.
To assemble printed circuit boards (PCBs) involves three basic steps: adhesive preparation, mounting and soldering. Adhesive preparation involves cleaning the board of all dust particles and removing excess adhesives. The second step is the mounting of the electronic components such as transistors, capacitors, diodes and other electrical connections. The final step is soldering and final assembly of the components. The number of steps in the assembly process of a printed circuit board (PCB) depends on the type of board and its specifications.
Types of Printed Circuit Boards The most common form of printed circuit boards (PCBs) includes Plastic, Dielectric, Polyvinyl Choloride (DVC) and Copper. PCBS may also be available in different thicknesses for different components. Low cost PCBSs may also be available. Printed circuit board (PCB) material selection includes dielectric, thermoplastic, epoxy, polyvinyl carbonate (PVC), PVC, and silverstein. Materials such as printed circuit boards (PCBs) are developed based on the applications they will be utilized for.
Components Size The components and sizes of printed circuit boards (PCBs) vary according to their usage. Some printed circuit boards (PCBs) are very small in size and can support only a single wire while others are large and can support thousands of wires. Components and their sizes affect the price of the product. Thus, it is important to select the appropriate components that can support the electronic components and make the product efficient and durable.
Relevant
Printed Circuit Boards


